News
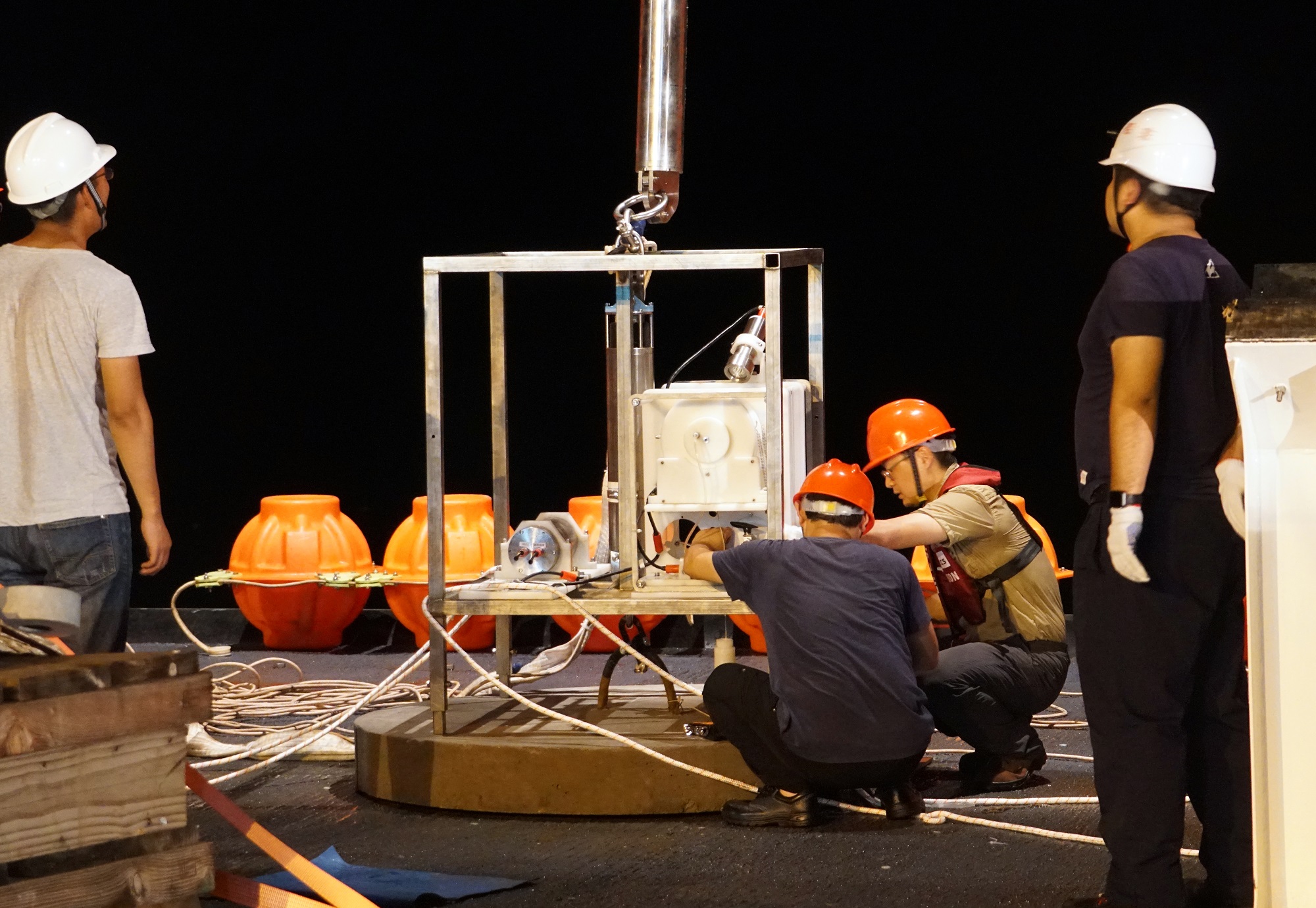
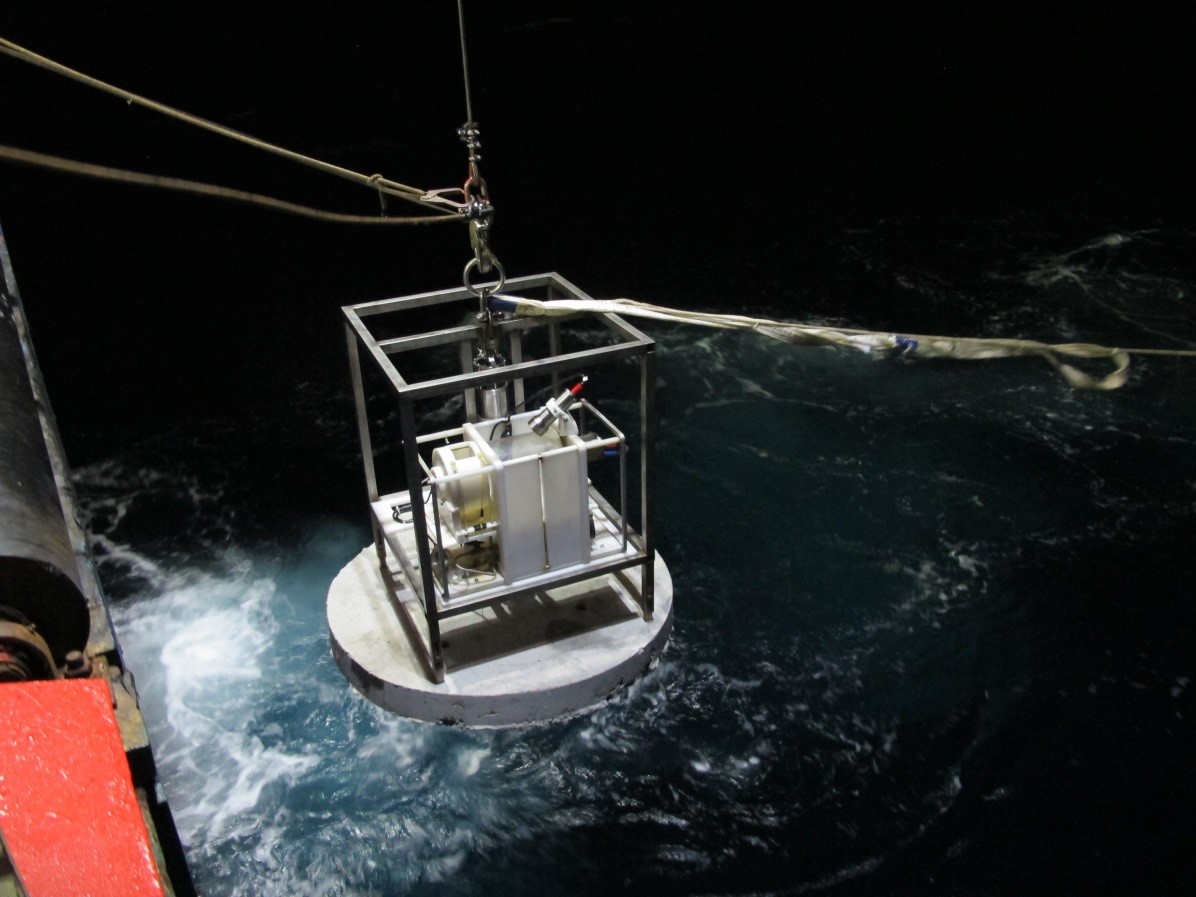

Recently, an important breakthrough has been made in the deep-sea in-situ artificial induction long-term observation device independently developed by SIO, and the deep-sea in-situ artificial construction similar to the initial habitat of cold spring has been realized for the first time in the world. The device was developed and completed by Zheng Minhui, a senior engineer at the Key Laboratory of Marine Ecosystem Dynamics of the Ministry of Natural Resources.
The device has been used in sea trials for many times, and cumulatively deployed in water depths of above 1,000 meters for as long as 17 months with a large number of culture and control water samples obtained. During the deployment of the device on the seabed, the photos showed that the multi-cellular organisms, hook shrimp and jellyfish entered the culture system for life. Among them, the hook shrimp lived in the culture system for a long time and was successfully captured with the water sample when the device was recovered. The results of further laboratory analysis of the water samples showed that there were significant differences in the microbial community composition between the culture water samples and the control water samples. The culture water samples contained archaea unique to cold spring habitats such as ANME-2a-2b and a variety of methane anaerobic oxidation archaea, which were not found in the control water samples. Based on the above results, it can be considered that the device has successfully induced an initial habitat similar to cold spring environment on the seabed. The academic paper "Artificial construction of the biocoenosis of deep-sea ecosystem via seeping methane" on device design, application and sample analysis research results has been published in Environmental Microbiology.
Based on the deep-sea in-situ artificial induction long-term observation device developed by the team, it can realize the artificial construction and long-term maintenance of special deep-sea ecosystems, transforming the traditional observation and investigation of deep-sea ecosystem research to scientific experiments with controllable and continuous biological processes, which provides an effective new strategy for revealing the mechanism of the origin of biological communities in deep-sea ecosystems. The device has achieved technological breakthroughs in the core components of deep-sea liquid injection reaction such as peristaltic pumps, laying a key technical foundation for the construction of a deep-sea long-term online experimental station with all-round capabilities of training, sampling and analysis. It is expected to provide a new technical means for the research of deep-sea life science and the excavation of deep-sea extreme environmental gene resources.



