News
Recently,Meng Qicheng, head of an offshore dynamic process and ecosystem team of statekey experiment of satellite marine environmental dynamics, has published anacademic paper on the Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, whichwas entitled "Impact of Submesoscale Vertical Advection on PrimaryProductivity in the Southern East China Sea". The corresponding authorsare associate researcher Xuan Jiliang and researcher Zhou Feng and co-authorsinclude research researcher Zhang Wenyan and Professor Corinna Schrum from theInstitute of Coastal Research of Helmholtz Association of German ResearchCenters.
Thisstudy uses a high-resolution physics-biogeochemical coupling model to assessthe impact of sub-mesoscale vertical convection on the primary productivity inthe southern East China Sea, quantitatively analyzes the relative contributionof the supply of nutrients by multi-scale physical processes to the euphoticzone, and points out that the sub-mesoscale vertical convection is the most importantvertical nutrient supply pathway in the southern East China Sea in summer.
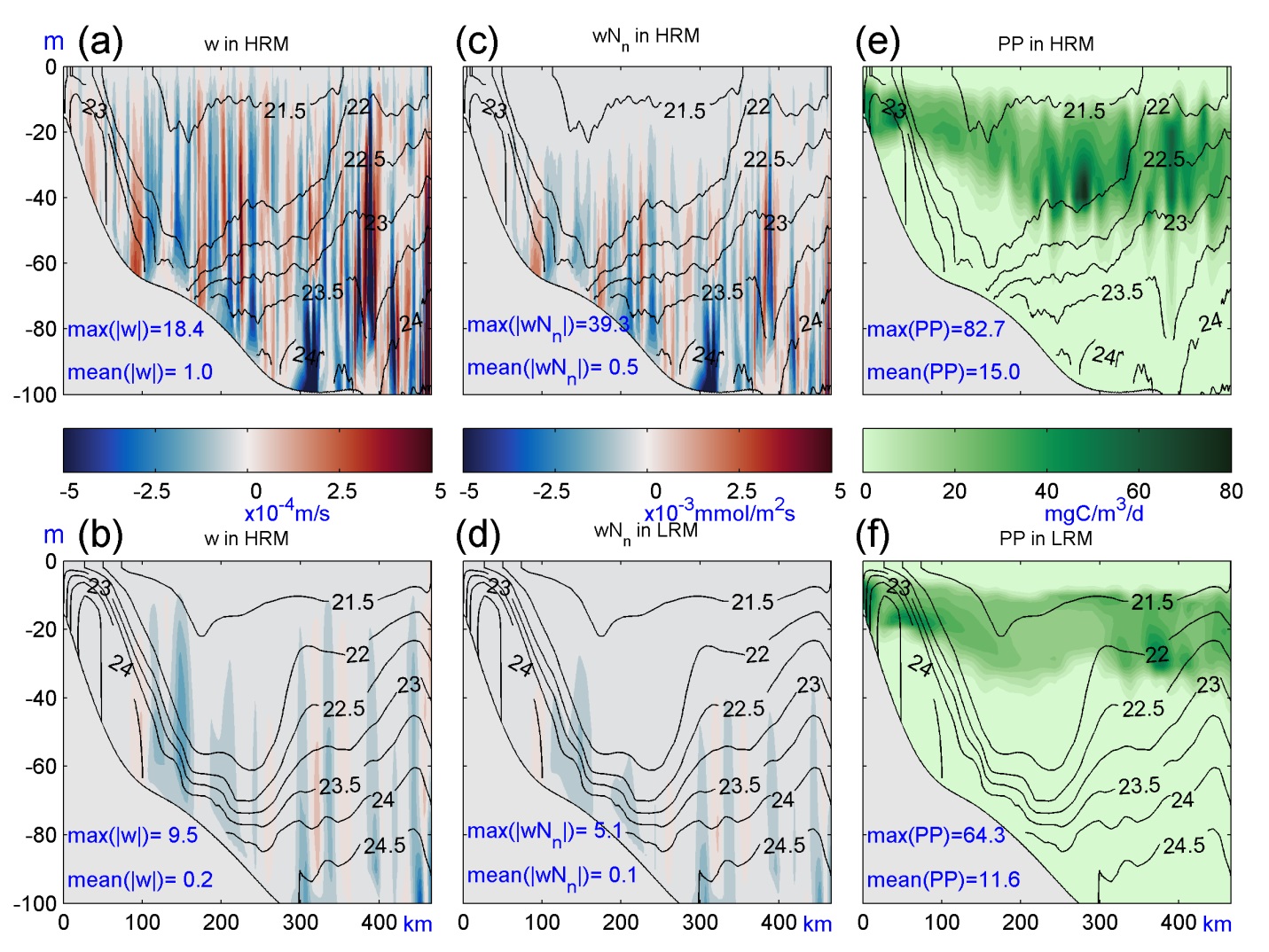
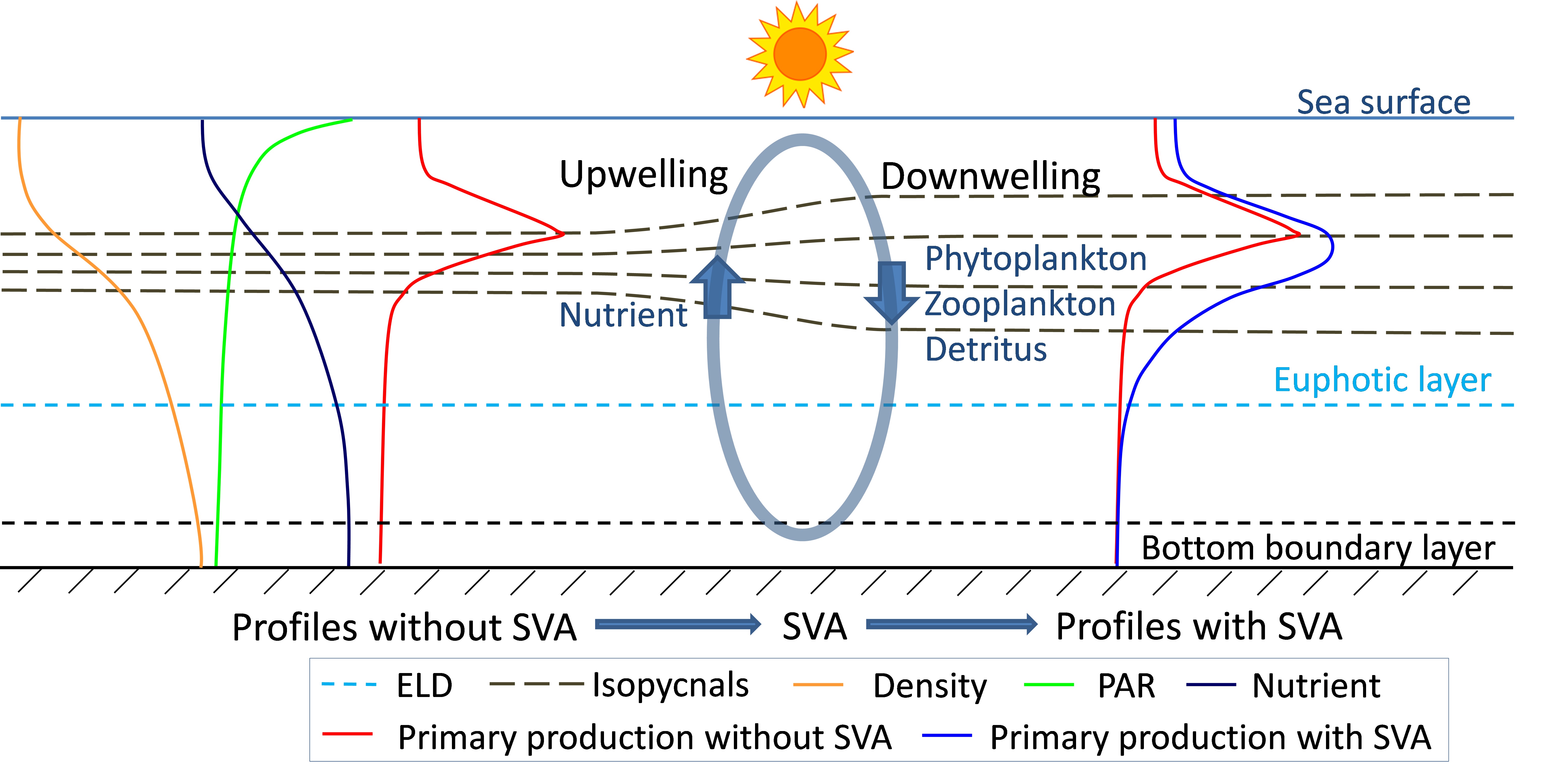
Studieshave shown that the water in the southern East China Sea is strongly stratifiedin summer, and nutrients are extremely lacking on the surface, while the deepseawater is rich in nutrients due to the invasion of the Kuroshio subsurfacewater across the shelf. At the time, the rapid vertical water exchange caused by thesub-mesoscale vertical convection can penetrate the nutrient thermocline(Figure 1c, d) and establish a vertical transport pathway for nutrients.Quantitative calculations show that the contribution of nutrient supply bysub-mesoscale vertical convection to the surface exceeds that of vertical turbulentdiffusion, becoming the most important vertical nutrient supply pathway insummer. Nutrients transported upward by sub-mesoscale vertical convection playa vital role in supporting primary productivity. The primary productivity insummer in the southern East China Sea obtained by the high-resolution model isabout 40% higher than that of the low-resolution model.
Inrecent years, the offshore dynamic process and ecosystem team has extensivelycarried out multidisciplinarycooperation and academic exchanges at home and abroad, focusing on the couplingrelationship between the dynamic process of the East China Sea and theecosystem, carrying out in-depth study of the dynamic changes of nutrientfluxes on the interfaces of the East China Sea, and exploring the mechanism ofalgal bloom, hypoxia and other ecological disasters and the monitoring andearly warning technology. The results have been published in mainstreamjournals such as Geophysical Research Letters, Progress in Oceanography,Journal of Geophysical Research, and Ocean Modeling, Frontiers in MarineScience, Ocean Science, Journal of Marine Systems and Science China.



